We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity-related products from Covalab
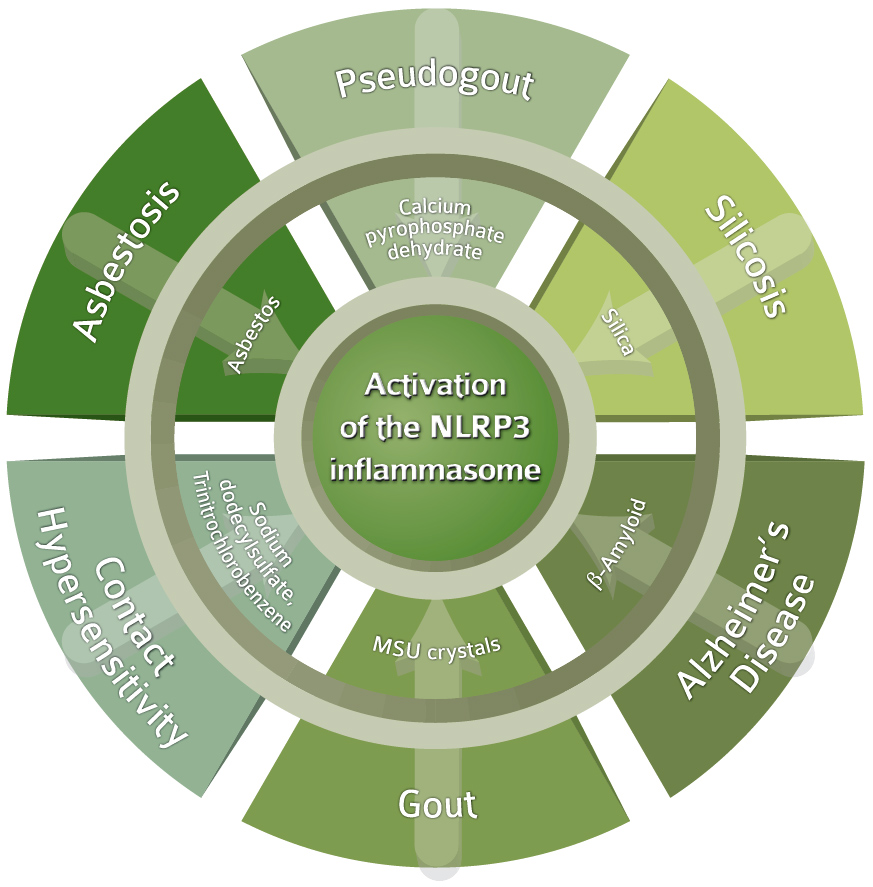
The exact sequence of events leading to activation of inflammasomes is not clear for all types of inflammasomes. The most prominent function of the NLRP3 inflammasome is the processing and activation of pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β). Yet most cells do not express pro-IL-1β and thus prior expression of pro-IL-1β is required. This can be achieved by stimulating receptors such as TLRs (e.g. LPS), NODs or TNF-Rs (e.g. TNF-α) that activate NF-κB and initiate pro-IL-1β transcription. This process of pro-IL-1β induction is called priming (signal 1). Priming also induces NF-κB-dependent transcription of NLRP3.
An additional stimulus (signal 2) results in the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and subsequent initiation of downstream signalling. In the absence of priming, NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent caspase-1 activation can also be observed, but IL-1β secretion is absent.