We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity-related products from Covalab
Inflammasomes are multi-protein complexes whose activity has been implicated in physiological and pathological inflammation. The hallmarks of inflammasome activation are the secretion of the mature forms of caspase-1 and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) from cells of the innate immune system.
An inflammasome represents a high molecular weight complex that activates inflammatory caspases and cytokines of the IL-1 family (IL-1β, IL-18 and depending on the stimulus also IL-1α). Several inflammasomes which contain different sensor proteins such as NLRP1 (NALP1), NLRP3 (NALP3), IPAF (NLRC4), NLRP6 (NALP6), RIG-I and AIM-2 (absent in melanoma 2) have been described.
Most of these inflammasomes require the adapter protein Asc (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain) to recruit caspase-1 to the inflammasome complex. Upon binding to the inflammasome, caspase-1 is cleaved and activated, leading to cleavage of its various targets and causing maturation and secretion of the proinflammatory IL-1β. Inflammasomes can be activated through multiple signals including live bacteria, microbial toxins, xeno-compounds, cytoplasmic pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and/or endogenous danger signals (DAMPs)
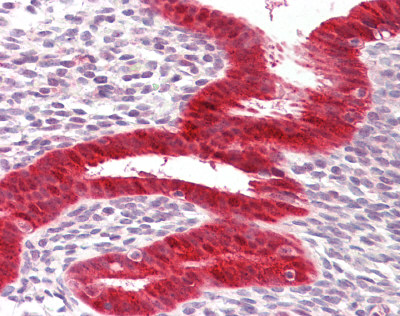
Anti-RIG-1 / RIG-I antibody IHC staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human uterus.
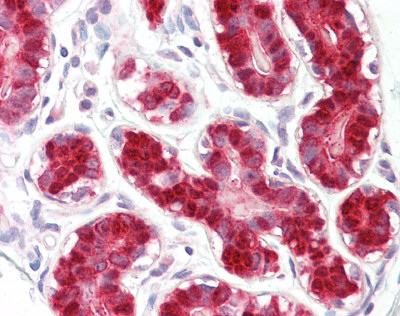
Anti-RIG-1 / RIG-I antibody IHC staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human breast.
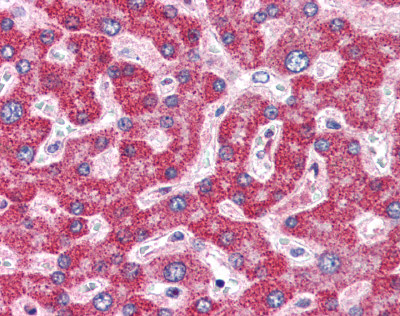
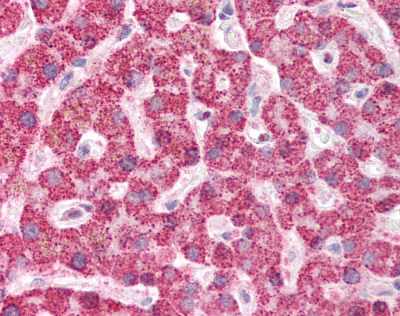
Anti-ZBP1 antibody IHC staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver.
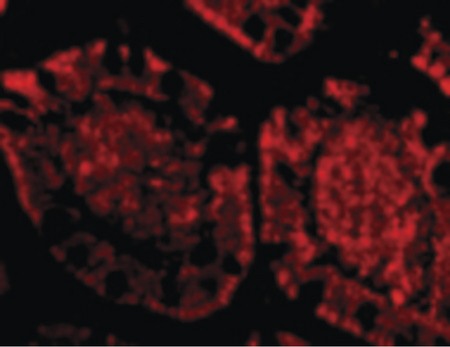
Anti-ZBP1 antibody IF staining of human small intestine cells.
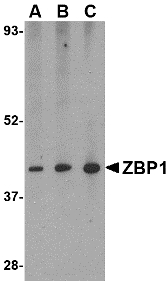
Anti-ZBP1 antibody WB staining of mouse small intestine tissue lysate.
Anti-MDA5 antibody IHC staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver.
